Efficient bulk material handling depends on the correct selection of equipment. Screw conveyors play a vital role in moving materials through bulk handling systems. Their design influences both performance and operational costs.
Material compatibility, throughput requirements, and maintenance needs serve as critical factors during the selection process. Choosing the right screw conveyor ensures smoother operations and cost-effective solutions.
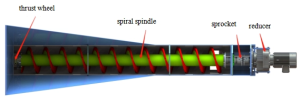
Overview of Screw Conveyor Designs
Screw conveyors come in various designs, each tailored to specific applications and material handling needs. Understanding the differences between these designs helps in selecting the most suitable option for optimal performance.
Shafted Screw Conveyors
The shafted screw conveyor is one of the most common mechanical conveyors. It features a central shaft that supports the screw, ensuring stability during operation. This design works well for transporting dry, granular materials over long distances.
Its enclosed structure minimizes spillage, making it ideal for industries requiring cleanliness. However, the presence of a shaft can limit its ability to handle sticky or fibrous materials effectively.
Shaftless Screw Conveyors
Unlike the shafted version, the shaftless screw conveyor eliminates the central shaft. This design increases the capacity to handle sticky, wet, or fibrous materials. It also reduces the risk of clogging.
These conveyors are often used in wastewater treatment plants and other industries dealing with challenging materials. However, they may require more frequent maintenance due to increased wear on the screw.
Flexible Screw Conveyors
Flexible screw conveyors offer versatility in material handling. Their flexible tube and screw allow them to transport materials at various angles and around obstacles. These conveyors are lightweight and easy to install, making them suitable for small-scale operations.
They work well with powders, granules, and other free-flowing materials. However, they may not be the best choice for abrasive or heavy materials due to potential wear on the screw.
Vertical Screw Conveyors
Vertical screw conveyors are designed to move materials upward. They are commonly used in applications requiring vertical lifts, such as silos or storage bins. These conveyors save floor space and provide efficient vertical transport.
However, they may have lower throughput compared to horizontal designs and require precise alignment for optimal performance.
Inclined Screw Conveyors
Inclined screw conveyors are used to transport materials at an angle. They are ideal for applications where space constraints prevent horizontal transport. The efficiency of these conveyors depends on the angle of inclination and the material being handled. While they are versatile, their performance may decrease at steeper angles due to material slippage.
Comparison of Advantages and Disadvantages
Shafted designs
The shafted screw conveyor offers robust performance for transporting dry and granular materials. Its central shaft provides stability, making it suitable for long-distance operations. This design minimizes spillage due to its enclosed structure, which is beneficial for industries requiring cleanliness.
However, the central shaft can restrict the movement of sticky or fibrous materials. Maintenance can also become challenging when dealing with materials that tend to accumulate around the shaft.
Shaftless designs
The shaftless screw conveyor excels in handling sticky, wet, or fibrous materials. Its open design eliminates the central shaft, reducing the risk of clogging. This makes it a preferred choice for wastewater treatment and other industries managing challenging materials.
Despite these advantages, the absence of a shaft increases wear on the screw, leading to higher maintenance needs. Additionally, this design may not perform as efficiently with dry or free-flowing materials.
Flexible screw conveyors
Flexible screw conveyors provide unmatched versatility. Their flexible tube and screw allow them to navigate around obstacles and operate at various angles. These conveyors are lightweight and easy to install, making them ideal for small-scale operations.
They work well with powders, granules, and other free-flowing materials. However, they are less effective with abrasive or heavy materials, as these can cause significant wear on the screw over time.
Material compatibility for each design
Each screw conveyor design offers unique compatibility with specific materials. The shafted screw conveyor is best for dry, granular materials. The shaftless screw conveyor handles sticky, wet, or fibrous materials effectively.
Flexible screw conveyors are suitable for free-flowing powders and granules but struggle with abrasive or heavy materials. Selecting the right design depends on the material’s properties and the operational requirements.
Industry-Specific Applications
Best designs for food and beverage industries
The food and beverage industry demands high standards of hygiene and precision. Flexible screw conveyors excel in this sector due to their ability to handle free-flowing materials like flour, sugar, and spices.
Their enclosed design prevents contamination, ensuring food safety. Additionally, these conveyors can transport materials at various angles, making them suitable for compact production spaces. Stainless steel construction is often preferred for its resistance to corrosion and ease of cleaning.
Optimal designs for construction and mining
Construction and mining industries require robust equipment to handle heavy-duty tasks. Shafted screw conveyors are ideal for transporting materials like sand, gravel, and cement over long distances.
Their sturdy design ensures durability under harsh conditions. For operations involving sticky or wet materials, shaftless screw conveyors provide a reliable alternative. These designs reduce the risk of clogging, ensuring uninterrupted material flow.
Applications in chemical and pharmaceutical industries
Chemical and pharmaceutical industries prioritize precision and material compatibility. Flexible screw conveyors are widely used for transporting powders or granules, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients or chemical additives.
Their versatility allows them to navigate complex layouts while maintaining consistent material flow. Non-reactive materials like stainless steel or specialized coatings are often used to prevent contamination and ensure safety.
Handling of abrasive or corrosive materials
Abrasive or corrosive materials pose unique challenges in material handling. Shaftless screw conveyors are well-suited for these applications due to their open design, which minimizes wear and tear.
For highly abrasive materials, reinforced screws and wear-resistant linings extend the equipment’s lifespan. Corrosive materials, such as chemicals or salts, require conveyors made from corrosion-resistant alloys to ensure durability and performance.
Conclusion
Selecting the right screw conveyor design depends on understanding its unique features and limitations. Each design serves specific material handling needs, from shafted models for dry materials to shaftless options for sticky substances.
Evaluating material compatibility, operational costs, and application requirements ensures optimal performance. Consulting experts or manufacturers can simplify the decision-making process.